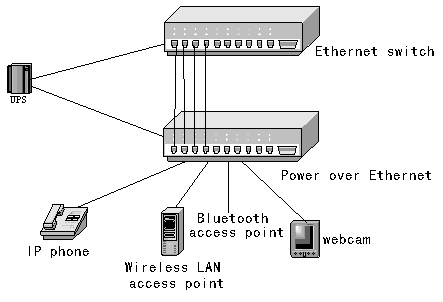
Overview of Power Over Electricity (POE)
POE (Power Over Ethernet) refers to some IP-based terminals (such as IP phones, wireless LAN access points AP, network cameras, etc.) without changing the existing Ethernet Cat.5 wiring infrastructure. While transmitting data signals, it provides DC power supply technology for such devices. POE technology can ensure the normal operation of the existing network while ensuring the safety of the existing structured cabling, and minimize costs.
POE is also known as a power supply system based on local area network (POL, Power over LAN) or Active Ethernet (Active Ethernet), sometimes also referred to as Power over Ethernet for short. This is to use existing standard Ethernet transmission cables to transmit data and data at the same time. The latest standards and specifications of electric power, and maintain compatibility with existing Ethernet systems and users. The IEEE 802.3af standard is a new standard based on the POE of the Power-over-Ethernet system. It adds related standards for direct power supply through network cables on the basis of IEEE 802.3. It is an extension of the existing Ethernet standard and the first international standard for power distribution. standard.
IEEE began to develop the standard in 1999, and the earliest participating vendors were 3Com, Intel, PowerDsine, Nortel, Mitel, and National Semiconductor. However, the deficiencies of this standard have been restricting the expansion of the market. Until June 2003, the IEEE approved the 802.3af standard, which clearly specified power detection and control issues in remote systems, and connected routers, switches, and hubs to IP phones, security systems, and wireless local area networks through Ethernet cables. Standardize the power supply mode of equipment such as points. The development of IEEE 802.3af includes the efforts of many company experts, which also allows the standard to be fully tested.
POE system composition and power supply characteristic parameters
A POE system includes power supply equipment (PSE, Power Sourcing Equipment) and power receiving equipment (PD, Power Device) parts. The PSE device is the device that supplies power to the two client devices, and it is also the device that supplies power to the entire POE. The PD device is the PSE that accepts power, that is, the client device of the POE system, such as IP phones, network security, APs, and PDAs. ) Or many other devices such as mobile phones and computers (small, any device with a power exceeding 13W can obtain the corresponding power from the RJ45 interface). It does not rely on the IEEE 802.3af standard to establish information connections about the connection status, device type, and level of the receiving end device PD, and at the same time provide power to the PD according to the PSE.
The main power supply characteristic parameters of the POE standard power supply system are:
◆The voltage is between 44V and 57V, with a typical value of 48V.
◆The maximum allowable current is 550mA, and the maximum starting current is 500mA.
◆The average working current is 10~350mA, and the overload current is 350~500mA.
◆Under no-load conditions, the maximum required current is 5mA.
◆Provide five levels of electrical power requests from 3.84 to 12.95W for PD equipment, with a maximum of no more than 13W.
The working process of POE power supply
When floating PSE power supply terminal equipment in a network, the working process of POE power supply is as follows.
◆Detection: At the beginning, the voltage output by the PSE device at the port until it detects that the data terminal connection is a power-receiving device that supports the IEEE 802.3af standard.
◆PD device classification: After detecting the power receiving device PD, the PSE device may classify the PD device and evaluate the power consumption required by the PD device.
◆Start power supply: At a configurable time (generally less than 15μs) to start the power supply, the PSE device starts to supply power to the PD device from a low voltage until it provides a 48V power supply.
◆Power supply: Provide stable and reliable 48V dynamic over-voltage for PD equipment to meet the power overtime of PD equipment that does not exceed 15.4W.
◆Power off: If the PD device is disconnected from the network, the PSE will quickly (usually within 30-400ms) stop powering the PD device, and repeat the detection process to detect whether the data terminal is connected to the PD device.
When connecting any network device to the PSE, the PSE must first detect that the device is not a PD to ensure that it does not provide current to devices that do not meet the POE standard, which may cause damage. It can be realized by looking for a small voltage of electric current to check whether the distance has the characteristics that meet the requirements. Only when the detection is reached can the full 48V voltage be provided, the current still exists, and the extremely short terminal equipment may have an error state. . As an extended PD of the discovery process, it can also classify the power supply modes that require the PSE, and provide the PSE to supply power in an efficient manner. The PSE starts to provide power. It will continue to monitor the PD input current. When the PD current consumption drops below the minimum value, such as when the device is unplugged or encounters excessive power consumption of the PD device, short circuit, or power supply load exceeding the PSE, the PSE will Destroy the power supply and start the detection process again.
The power supply device can also be provided with a system capability, for example, the application of simple network protocol (SNMP). The function can provide functions such as recovery recovery and recovery recovery management.
It is possible to study the transmission mode of POE. There are two key issues to consider in the process of providing, which is the identification of PD equipment, and the other is the ability of UPS in the system.