Foreword: Communication fiber is divided into single mode fiber and multimode fiber according to the number of transmission modes under its application wavelength.Due to the large core diameter of the multimode fiber, it can be used with low cost light sources. Therefore, it has a wide range of applications in short-distance transmission scenarios, such as data centers and local area networks.With the rapid development of data center construction in recent years, multimode fiber, which is the mainstream of data center and local area network applications, has also ushered in the spring, causing widespread concern.Today, let’s talk about the development of multimode fiber.
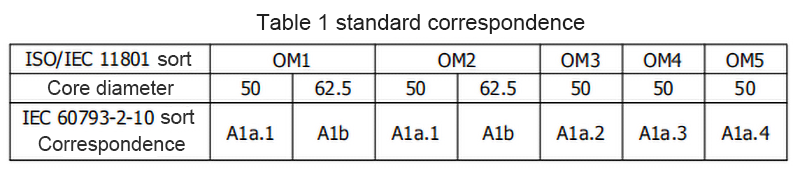
According to the standard ISO/IEC 11801 specification, multimode fiber is divided into five major categories: OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5.Its correspondence with IEC 60792-2-10 is shown in Table 1.Among them OM1, OM2 refers to the traditional 62.5/125mm and 50/125mm multimode fiber. OM3, OM4 and OM5 refer to the new 50/125mm 10 Gigabit multimode fiber.
First: the traditional multimode fiber
The development of multimode fiber began in the 1970s and 1980s. Early multimode fibers included many sizes, and four types of sizes included in the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards included four.The core cladding diameter is divided into 50/125 μm, 62.5/125 μm, 85/125 μm, and 100/140 μm.Due to the large size of the core cladding, the manufacturing cost is high, the bending resistance is poor, the number of transmission modes is increased, and the bandwidth is reduced. Therefore, the type of the large core cladding size is gradually eliminated, and two main core cladding sizes are gradually formed. They are 50/125 μm and 62.5/125 μm, respectively.
In the early local area network, in order to reduce the system cost of the local area network as much as possible, a low-cost LED was generally used as a light source.Due to low LED output power, the divergence Angle is relatively large. However, the core diameter and numerical aperture of the 50/125mm multi-mode fiber are relatively small, which is not conducive to efficient coupling with LED. As for the 62.5/125mm multi-mode fiber with large core diameter and numerical aperture, more optical power can be coupled to the optical link.Therefore, 50/125mm multimode fiber was not as widely used as the 62.5/125mm multimode fiber before the mid-1990s.
With the continuous increase of LAN transmission rate, since the end of the 20th century, the LAN has been developed above the lGb/s rate. The bandwidth of 62.5/125μm multimode fiber with LED as the light source is only gradually unable to meet the requirements.In contrast, the 50/125mm multimode fiber has a smaller numerical aperture and core diameter, and fewer conduction modes.Therefore, the mode dispersion of multi-mode fiber is effectively reduced, and the bandwidth is significantly increased. Due to the small core diameter, the production cost of 50/125mm multi-mode fiber is also lower, so it is widely used again.
The IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet standard specifies that 50/125mm multimode and 62.5/125mm multimode fibers can be used as transmission media for Gigabit Ethernet. However, for new networks, 50/125mm multimode fiber is generally preferred.
Second:laser optimized multimode fiber
With the development of technology, 850 nm VCSEL (Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser) appeared.VCSEL lasers are widely used because they are cheaper than long-wavelength lasers and can increase network speeds.VCSEL lasers are widely used because they are cheaper than long-wavelength lasers and can increase network speeds.Due to the difference between the two types of light-emitting devices, the fiber itself must be modified to accommodate changes in the light source.
For the needs of VCSEL lasers, the International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission (ISO/IEC) and the Telecommunications Industry Alliance (TIA) have jointly drafted a new standard for multimode fiber with a 50mm core.ISO/IEC classifies a new generation of multimode fiber into the OM3 category (IEC standard A1a.2) in its new multimode fiber grade, which is a laser-optimized multimode fiber.
The subsequent OM4 fiber is actually an upgraded version of OM3 multimode fiber.Compared with OM3 fiber, the OM4 standard only improves the fiber bandwidth index.That is, the OM4 fiber standard has improved the effective mode bandwidth (EMB) and the full injection bandwidth (OFL) at 850 nm compared to the OM3 fiber. As shown in Table 2 below.
There are many modes of transmission in multimode fiber, and the problem of bending resistance of the fiber is also brought about. When the fiber is bent, the high-order mode is easily leaked, resulting in loss of signal, that is, bending loss of the fiber.With the increasing number of indoor application scenarios, the wiring of multimode fiber in a narrow environment has put forward higher requirements for its bending resistance.
Unlike the simple refractive index profile of a single-mode fiber, the refractive index profile of a multimode fiber is very complex, requiring an extremely fine refractive index profile design and fabrication process.In the current four major prefabrication process of the international mainstream, the most precise preparation of multimode fiber is the plasma chemical weather deposition (PCVD) process, represented by Changfei Company.This process differs from other processes in that it has a deposition layer of several thousand layers and a thickness of only about 1 micron per layer during deposition, enabling ultra-fine refractive index curve control to achieve high bandwidth.
By optimizing the refractive index profile of multimode fiber, the bending-insensitive multimode fiber has a significant improvement in bending resistance, as shown in Figure 1 below.
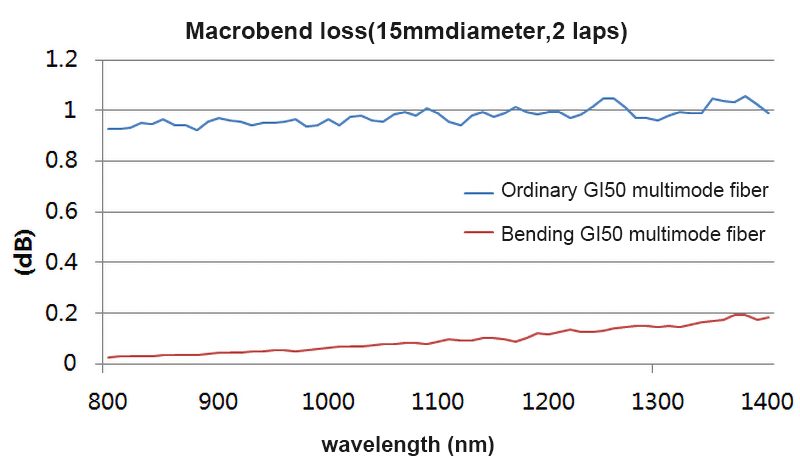
Fig.1 Comparison of macrobend performance between bending-resistant multimode fiber and conventional multimode fiber
Third:the new multimode fiber (OM5)
OM3 fiber and OM4 fiber are multimode fiber mainly used in the 850nm band.As the transmission rate continues to increase, only a single-channel band design will result in more and more intensive wiring costs, and the associated management and maintenance costs will increase accordingly.Therefore, the technicians try to introduce the wavelength division multiplexing concept into the multimode transmission system. If multiple wavelengths can be transmitted on one fiber, the corresponding number of parallel fiber and the cost of laying and maintenance can be greatly reduced.In this context, OM5 fiber came into being.
OM5 multimode fiber is based on OM4 fiber, which widens the high-bandwidth channel and supports transmission applications from 850nm to 950nm.The current mainstream applications are SWDM4 and SR4.2 designs. SWDM4 is a wavelength division multiplexing of four short waves, which are 850 nm, 880 nm, 910 nm, and 940 nm, respectively.In this way, an optical fiber can support the services of the previous four parallel optical fibers. SR4.2 is a two-wavelength division multiplexing, mainly used for single-fiber bidirectional technology.The OM5 can be matched with VCSEL lasers with low performance and low cost to better meet short-distance communication such as data centers.Table 3 below is a comparison of the main bandwidth specifications for OM4 and OM5 fibers.
At present, OM5 fiber has been used as a new type of high-end multimode fiber.One of the largest business cases is the OM5 commercial case of Changfei and China Railways Corporation’s main data center.The data center is aiming at the application advantages of OM5 fiber in the wavelength division system of SR4.2. It achieves the maximum capacity communication at the lowest cost, and prepares for further upgrade rate in the future. The future rate will be increased to 100Gb/s or even 400Gb. /s, or wideband applications, can no longer replace fiber, significantly reducing future upgrade costs.
Summary: As the demand for applications continues to increase, multimode fiber is moving toward low bend loss, high bandwidth, and multi-wavelength multiplexing.Among them, the most potential application is OM5 fiber, which has the optimal performance of current multimode fiber, and provides a powerful fiber solution for multi-wavelength systems of 100Gb/s and 400Gb/s in the future.In addition, in order to meet the requirements of high-speed, high-bandwidth, low-cost data center communication, new multimode fibers, such as single multimode general-purpose fibers, are also being developed.In the future, Changfei will launch more new multimode fiber solutions with industry peers, bringing new breakthroughs and lower costs to data centers and fiber optic interconnects.