1. EPON network introduction
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) is an emerging optical fiber access network technology, which adopts point-to-multipoint structure, passive optical fiber transmission mode, based on high-speed Ethernet platform and TDM time division MAC (MediaAccessControl) media access control mode , Provide a variety of broadband access technologies for integrated services. The so-called “passive” means that the ODN does not contain any active electronic devices and power supplies, and all consists of passive devices such as optical splitters (Splitter). It uses PON technology at the physical layer, Ethernet protocol at the link layer, and uses the PON topology to achieve Ethernet access. Therefore, it combines the advantages of PON technology and Ethernet technology: low cost, high bandwidth, strong scalability, flexible and fast service reorganization, compatibility with existing Ethernet, convenient management, and so on.
EPON can realize the integration of voice, data, video, and mobile services. The EPON system is mainly composed of OLT (optical line terminal), ONU (optical network unit), ONT (optical network terminal) and ODN (optical distribution network). It is at the access network level of the network and is mainly suitable for optical fiber connection of broadband services. Into.
Active network equipment includes central office rack equipment (OLT) and optical network unit (ONU). The optical network unit (ONU) provides users with an interface between data, video, and telephone networks and the PON. The initial role of ONU is to receive the optical signal and then convert it into the format required by the user (Ethernet, IP broadcast, telephone, T1/E1, etc.). OLT equipment is connected to the IP core network through optical fiber. The introduction of the optical access network has a coverage of up to 20km, which ensures that the OLT can be upgraded to the traditional metropolitan convergence node from the initial stage of the optical access network construction, thus simplifying the network structure of the convergence layer of the access network and saving The number of end offices. In addition, the characteristics of the optical access network’s large capacity, high access bandwidth, high reliability, and multi-service QoS level support capabilities have also made the evolution of the access network towards a unified, integrated, and efficient bearer platform a reality.
2. Basic Principles of EPON Network
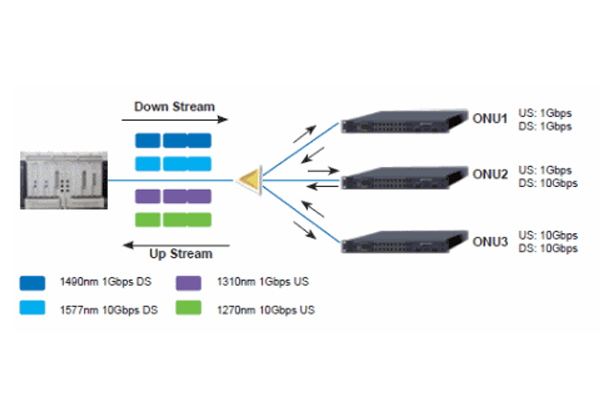
The EPON system uses WDM technology to realize single-fiber bidirectional transmission, using upstream 1310nm and downstream 1490nm wavelengths to transmit data and voice, and CATV services use 1550nm wavelength to carry. The OLT is placed in the central office to distribute and control the connection of the channel, and has real-time monitoring, management and maintenance functions. The ONU is placed on the user side, and the OLT and the ONU are connected in a 1:16/1:32 manner through a passive optical distribution network. In order to separate the signals from multiple users on the same fiber, the following two multiplexing techniques can be used.
(1) The downstream data stream adopts broadcasting technology. In EPON, the process of downstream data transmission from the OLT to multiple ONUs is sent by data broadcasting. Data is broadcast downstream from the OLT to multiple ONUs in the form of variable-length information packets. Each information packet has an EPON packet header, which uniquely identifies whether the information packet is sent to ONU-1, ONU-2 or ONU-3. It can also be marked as a broadcast information packet sent to all ONUs or to a specific ONU group (multicast information packet). When the data arrives at the ONU, the ONU receives and recognizes the information packets sent to it through address matching, and discards the information packets sent to other ONUs. A unique LLID is allocated after the ONU is registered; the OLT compares the LLID registration list when receiving data, and when the ONU receives data, it only receives frames or broadcast frames that match its own LLID.
(2) Upstream data flow adopts TDMA technology. The OLT compares the LLID registration list before receiving data; each ONU sends a data frame in the time slot uniformly allocated by the central office equipment OLT; the allocated time slot (through ranging technology) compensates for the gap in the distance of each ONU and avoids each ONU Collision between.