If the optical module does not have a fiber jumper, the fiber network connection cannot be achieved. Due to the different transmission media of the optical module, the fiber interface, transmission distance and data rate will be different.It is not difficult to identify these optical modules, but it takes some thought to match the optical modules with the appropriate fiber jumpers.
Optical modules are generally classified into copper-based electrical modules and optical optical modules according to different transmission media. MSA defines several electrical interface modules, such as 100BASE-T, 1000BASE-T, and 10GBASE-T. The electrical port module generally uses GBIC, SFP and SFP + standard and RJ45 interface. Usually, the electrical port module is connected by Cat5/6/7 network cable.
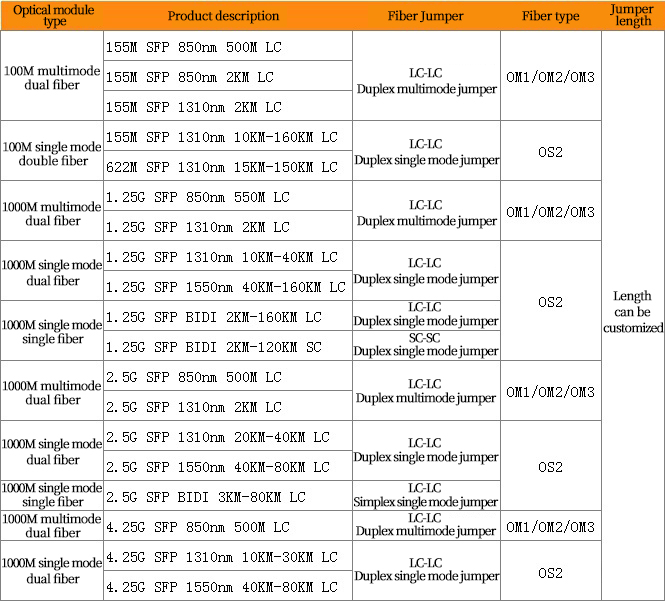
The following figure details the commonly used SFP optical modules and the types of jumpers that you need to match.
In selecting the fiber jumper, the interface problem of the optical module is first considered. The optical module is usually a port receiving and a port sending, and adopts a duplex LC or SC interface, so it is matched with a duplex optical fiber jumper. However, for the BiDi single-fiber optical module, one port can handle both receiving and transmitting functions, so the BiDi single-fiber transceiver module is used together with the simplex jumper.
Secondly, the fiber type, the fiber jumper is divided into single mode and multimode, the single mode jumper can be divided into OS1 and OS2, and the multimode fiber jumper can be divided into OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4. Different jumpers are used for different usage scenarios. Single-mode fiber jumpers can support long-distance transmission and single-mode optical modules. Multimode fiber jumpers can be used to connect short-range links to multi-mode optical modules.