Optical fiber transceiver is a flexible and effective photoelectric conversion device that plays an important role in multi-protocol photoelectric hybrid LAN. Now, in order to better detect and eliminate link faults, some optical fiber transceivers have link fail over (LFP) and remote fault (FEF) alarm functions.
Before we begin to describe the link failure over (LFP) and remote failure (FEF) alarm functions of fiber transceivers, it is necessary to understand the role of fiber transceivers in local area networks
Optical fiber transceiver has both electrical and optical ports, which are commonly used to connect optical port switches and electrical port switches to realize photoelectric conversion between two devices, as shown in the figure below:
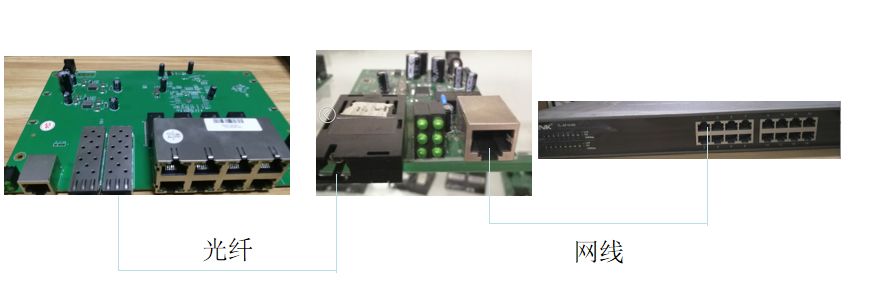
Of course, the main function of optical fiber transceiver is to convert light to electricity, as a bridge between two devices that cannot directly communicate, but its role is far more than that.
When the fiber transceiver is used in pairs, the cables used include at least two fiber optic cables and two cables (as shown below). It is the complexity of this cabling that leads to the link failover (LFP) and distal fault (FEF) alarm functions of the fiber transceiver.
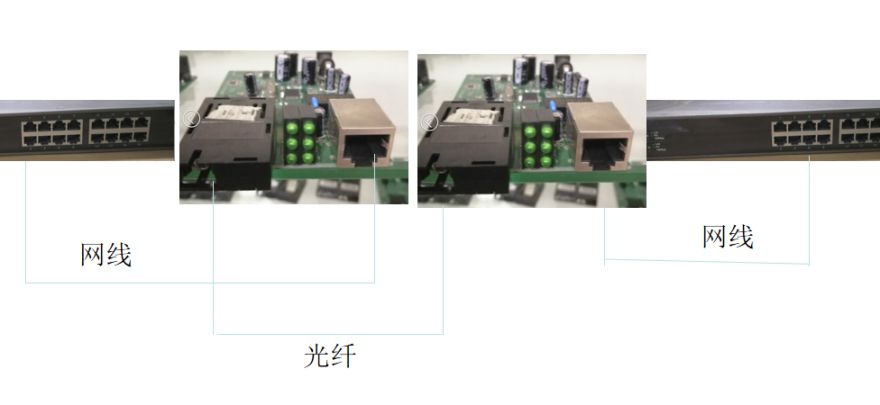
Link failover (LFP) refers to two connected communication devices (transceivers, switches, routers, etc.). One (near end) has A link fault, and the link fault can be transmitted to the other (remote) device. For example, two optical fiber transceivers A and B have A link fault in the electrical port of the transceiver A, and the transceiver will transmit the fault of the electrical port to the optical port. The transceiver will stop sending data from the optical port; If the transceiver at end B fails to receive the data from the transceiver at end A, it knows that the transceiver at end A has A link failure, and the transceiver at end B stops sending data from the optical and electrical ports. The link Failure Over (LFP) alarm enables network administrators to quickly know and handle network faults and reduce losses caused by network faults
Remote failure (FEF) refers to the failure of the optical cable that sends data from fiber optic transceiver A to fiber optic transceiver B, and the optical port of fiber optic transceiver A stops sending data to the optical port of fiber optic transceiver B. If the other cable is working properly, the optical port of the B transceiver continues to send data to the optical port of the A transceiver, causing a network failure. The role of the Remote Failure (FEF) alarm function is to reflect this problem.
The above is the explanation of transceiver LFP and FEF functions brought by Shenzhen HDV Phoelectron Technology Co., LTD. Our related network equipment has ONU series, OLT series, optical module series, welcome to further consultation.





