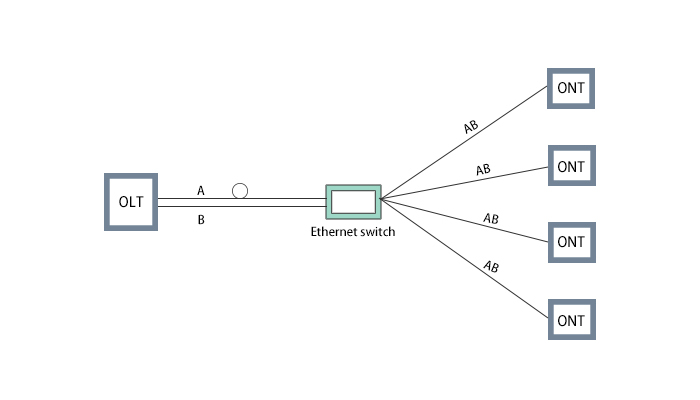
What is AON?
AON is an active optical network, mainly adopts a point-to-point (PTP) network architecture, and each user can have a dedicated optical fiber line. Active optical network refers to the deployment of routers, switching aggregators, active optical equipment and other switching equipment between central office equipment and user distribution units during signal transmission. These switchgears are driven by electricity to manage signal distribution and direction signals for specific customers. Active optical equipment includes light source (laser), optical receiver, optical transceiver module, optical amplifier (fiber amplifier and semiconductor optical amplifier).
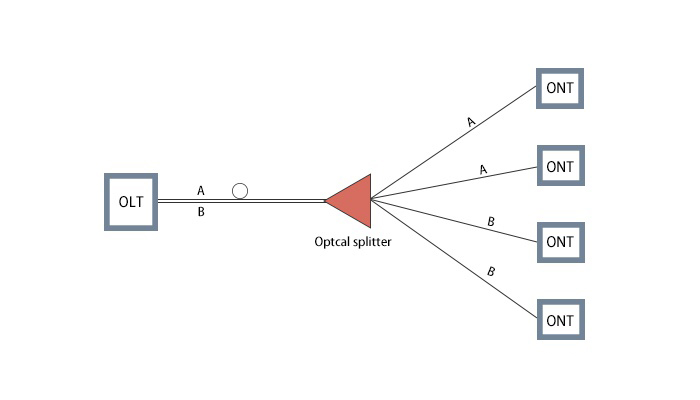
What is PON?
PON is a Passive Optical Network, a point-to-multipoint network structure, and is the main technology for FTTB/FTTH. Passive optical network refers to ODN (optical distribution network) only uses optical fibers and passive components, and only needs to use live equipment at the signal source and signal receiving end. In a typical PON system, the optical splitter is the core, and the optical splitter is used to separate and collect the optical signals transmitted through the network. These splitters for PON are bidirectional. In the downstream direction, multiple services such as IP data, voice, and video are distributed by the OLT located in the central office in the broadcast mode through the 1:N passive optical splitter in the ODN To all ONU units on the PON; in the upstream direction, multiple service information from each ONU is coupled to the same optical fiber through the 1:N passive optical combiner in the ODN without interfering with each other, and finally sent to the OLT at the central office for reception end.
A passive optical network includes an optical line terminal (OLT) installed at the central control station, and a group of matching optical network units (ONUs) installed at the user site. The optical distribution network (ODN) between the OLT and the ONU contains optical fibers and passive splitters or couplers. PON is divided into three technical standards: ATM-based APON (ATM PON), Ethernet-based EPON (Ethernet PON), and GPON (Gigabit PON) based on General Frame Protocol.
In the AON network, the user has a dedicated optical fiber line, which is easy for later network maintenance, capacity expansion, network upgrade, etc. In addition, the AON network covers a wide range of approximately 100 kilometers; the PON network is usually limited to fiber optic cables up to 20 kilometers. AON mainly guides optical signals through active devices, and PON uses passive devices without power supply, which results in higher costs for AON network deployment than PON.